In daily production, we often hear which types of bearings are very resistant to high temperatures, and which types can only be used in lower temperature environments.
The bearing temperature value is mainly determined by the material of the bearing. Different varieties and materials have different corresponding temperature endurance capabilities.
High-temperature bearings
High-temperature bearings refer to bearings that can withstand high temperatures. There are many types of high-temperature-resistant bearings. Different types of bearings can be installed according to different needs and environments. According to the structure, it can be divided into ordinary structure high-temperature bearings and special structure high-temperature bearings.
-
Temperature grade of high-temperature bearings
(1) The general temperature grades of 0~600 high-temperature bearings are divided into 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600. The commonly used temperature grades are 300 and 500.
(2) 600~800 high-temperature bearings. This type of high-temperature bearings are generally divided into full high-temperature steel high-temperature resistant bearings and ceramic hybrid high-temperature bearings.
(3), 800–1200 high temperature bearings. These bearings generally use silicon nitride ceramics as raw materials to replace steel in high-temperature environments that are difficult to reach.
The temperature classification of high-temperature bearings is as follows:
- Ordinary bearing steel can withstand high temperatures: 150-200℃
(The structure is full of rolling elements, which has a short service life and high subsequent maintenance costs)
- High-temperature alloy steel: 300-500℃
(The structure includes a cage and full rolling elements; the service life is more than one year, recommended)
- Silicon nitride ceramic rolling element: 800-1200℃
(Its structure is full of rolling elements, has a long service life and high cost) If your usage environment does not exceed 500℃, you can use the second material.
The high-temperature bearing method must be selected according to the actual application environment, such as a harsh environment and high speed. It must contain a cage, sealing ring, and imported high-temperature grease.
-
Structural classification of high-temperature bearings
2.1. Conventional bearing structure
Because high-temperature bearings with this type of structure do not have cages, the increased number of rolling elements greatly increases the bearing’s heavy-load and low-speed characteristics and has a longer service life. The applicable temperature range for high-temperature bearings is 0-800.
However, the disadvantage is that the limit speed of this type of high-temperature bearing is low, generally no more than 100r/min, and it will be even lower for bearings with larger inner diameters. Categories that meet this type of bearing conditions include deep groove ball bearings, aligning ball bearings, single-row cylindrical roller bearings and outer spherical ball bearings.
It should be noted that the high speed mentioned here does not mean that the bearing can reach a high limit speed, but that relative to “full rolling element high-temperature bearings”, affected by factors such as bearing clearance, it can generally reach 70% for ordinary bearings or 80% of the national standard limit speed. This type of bearing can withstand a temperature range within 600°C.
2.2. Full ceramic or hybrid ceramic bearings
Ceramic bearings can generally withstand high temperatures, and the ultimate temperature can reach 1,200.
However, it can only be achieved with ceramic cages, graphite cages or no cages. The temperature resistance of hybrid ceramic bearings (steel inner and outer rings and ceramic balls) is lower. If paired with a steel cage, it can only reach the limit of 600. temperature, but due to the high hardness and light weight of ceramic balls.
Low-temperature bearings
Low-temperature bearings are not correspond to high-temperature bearings and are bearings that can operate stably in high-temperature environments. Instead, they are designed to reduce the friction coefficient through special materials and structures, thereby reducing frictional heat and allowing the bearings to remain low-temperature during long-term operation…
-
Low temperature bearing operating temperature
Bearings with operating temperatures below -60°C are low-temperature bearings. It is mainly used in various types of liquid pumps, such as liquefied natural gas pumps, liquid nitrogen (hydrogen, oxygen) pumps, butane pumps, and liquid pumps for rocket missiles, spacecraft, etc.
The operating temperature of low-temperature bearings reflects the material technology and processing level of bearing processing. Its measurement is mainly based on the temperature difference between the bearing outer ring and the injected cooling oil during operation.
Cooler operating temperatures mean longer bearing life and higher performance. The world’s leading bearing manufacturers rely on their respective advantages and strive to obtain comparative advantages in low-temperature bearings in many fields. Take Timken spherical roller bearings as an example. After rigorous testing, the operating temperature of this company’s products is lower than similar products on the market, about 15.5 degrees Celsius, while other internationally renowned brands are above 19 degrees Celsius.
-
Product categories of low-temperature bearings
Low-temperature bearings are mostly single-row deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings.
For bearings stuck at low temperatures, the external factor is the temperature change, and the internal factor is the different thermal expansion coefficients of the shaft, frame and material. When the temperature range is large, different materials have different shrinkage rates, causing the gap to become smaller and stuck.
Therefore, for equipment with a wide working range, including equipment used at low temperatures, it is necessary to calculate the expansion coefficient of the material, and at the same time try to use materials with similar expansion coefficients, the effect will be better.
-
Material selection for low-temperature bearings
Low-temperature bearings are commonly made of stainless steel bearing steel 9Cr18, 9Cr18Mo, and can also be made of beryllium bronze, ceramics and other materials; under extremely low operating temperature conditions (limit temperature -253°C): when the working limit temperature is -253°C, 6Cr14Mo material can be used. Still, it must be used in a vacuum environment.
Note: When using low-temperature bearings, attention should be paid to burns caused by poor lubrication, so pay attention to selecting appropriate lubricants.
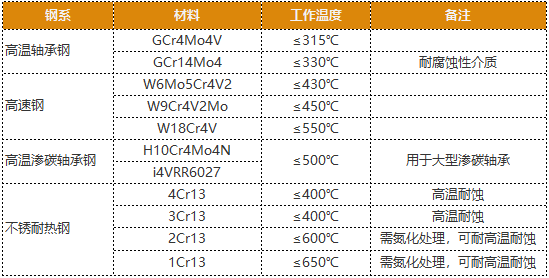
List of bearing materials and operating temperatures








Leave A Comment